Robotic Disassembly of E-waste
This project aimed at developing an autonomous robotic system for recycling of e-waste, particularly phones, tablets and watches. This was done as a part of the Biorobotics lab of Carnegie Mellon University Robotics Institute, in collaboration with Apple. The work involved developing an extension to apples ‘Daisy’ and ‘Dave’ robots that autonomously disassembles electronic devices.
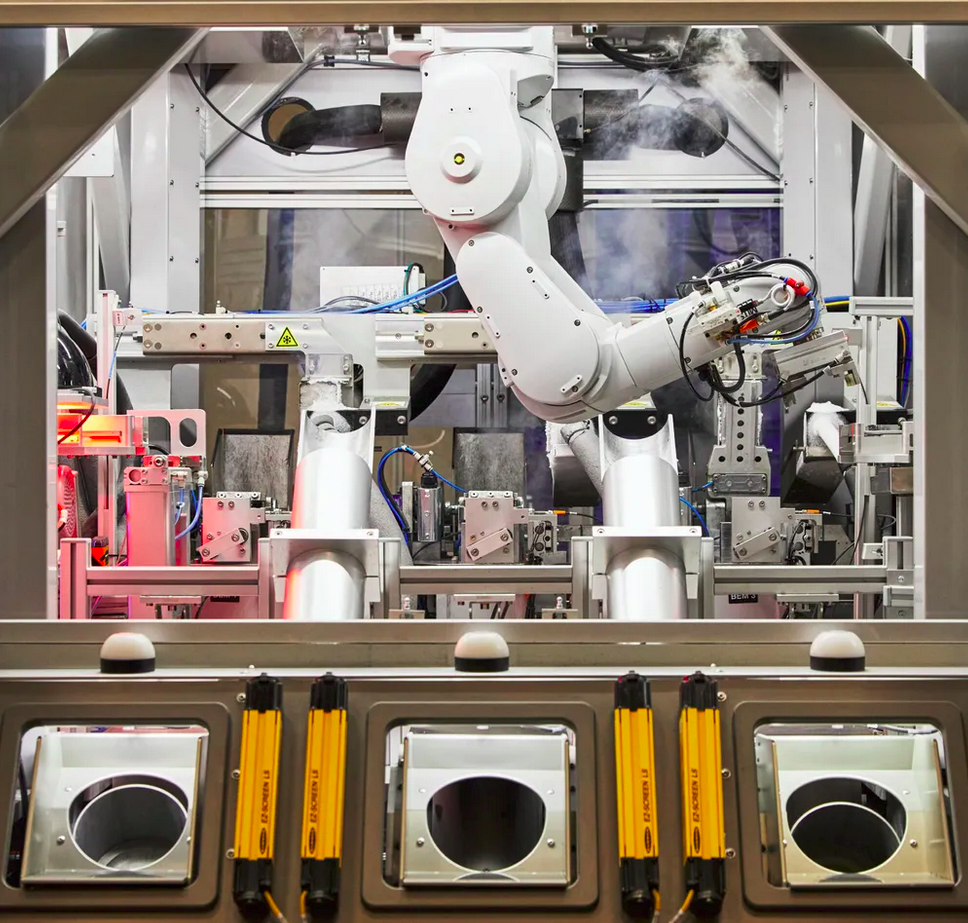


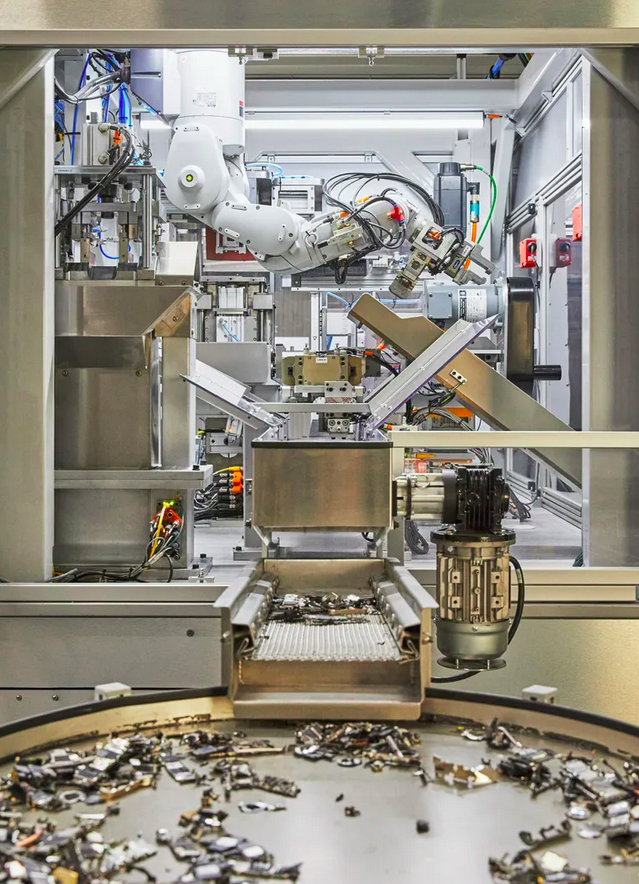
The project involved identifying and locating electronic components, such as cameras, screws, speakers, batteries, etc. in phones, tablets and watches. Several novel techniques were developed for synthetic dataset generation for segmentation and classification of RGB and X-ray images. These included methods that used domain randomization, synthetic deformation, slicing of CT-scans, stc. A novel classification algorithm iCAM was developed and trained using continual learning methods to progressively include new electronic devices. Novel segmentation approaches that rely on cross-attention and contrastive learning were also developed as a part of this effort.
Role in Project: Multimodal classification, semantic understanding of X-ray images, synthetic dataset generation, and designing & implementing the full ROS architecture
